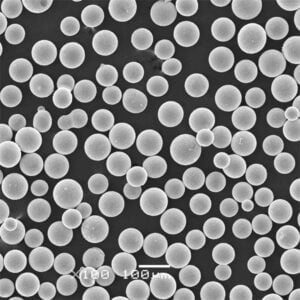
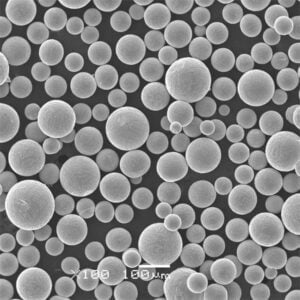
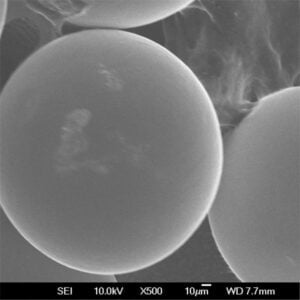
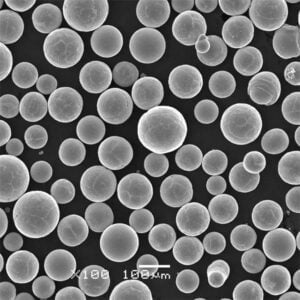
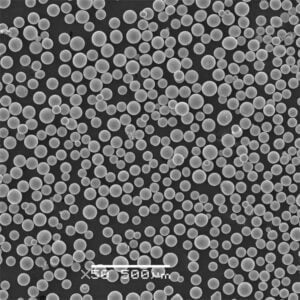
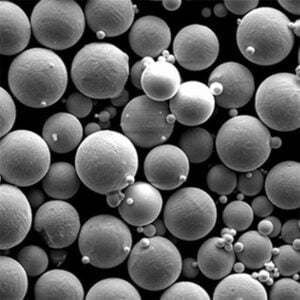
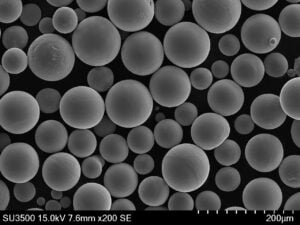
고밀도 텅스텐 분말 텅스텐은 금에 근접하는 매우 높은 고유 밀도 덕분에 모든 금속 분말 중에서 밀도가 가장 높습니다. 이러한 고유한 특성 덕분에 다양한 분야에서 고강도 분말 압착 및 소결 방법을 활용하여 컴팩트하고 무게 효율적인 부품을 설계할 수 있습니다.
개요 텅스텐 분말의
고체 형태의 밀도가 19.3g/cm3인 텅스텐은 작은 부피에 엄청난 무게를 담을 수 있습니다. 따라서 텅스텐 분말을 압축하면 다른 어떤 재료로도 달성할 수 없는 탁월한 밀도 수준을 제공합니다. 고밀도 텅스텐 분말로 만든 부품은 까다로운 환경에서 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다.
고밀도 텅스텐 분말을 활용하는 주요 동인은 다음과 같습니다:
- 금, 백금과 같은 귀금속과 유사한 고밀도
- 납, 강철에 비해 사용 가능한 밀도가 두 배 증가합니다.
- 무겁지만 컴팩트한 크기와 모양 구현
- 최종 사용 품목에 대한 간단한 분말 야금 경로
- 합금 원소를 혼합하여 맞춤형 속성 제공
- 고부가가치 텅스텐의 재활용성
밀도 스팬 밸러스트, 방사선 차단, 관성, 복합재 가중치, 진동 감쇠, 부품 소형화를 활용하는 애플리케이션입니다.

고밀도 텅스텐 분말의 종류
모든 텅스텐 분말 종류가 고밀도를 제공하지만, 특정 등급과 조성은 성형 및 소결 후 최적의 밀도 수준을 제공합니다:
| 유형 | 설명 | 일반적인 밀도 |
|---|---|---|
| 순수 텅스텐 | 99.95% 이상의 고순도로 안정적인 밀도 보장 | ≥18g/cm |
| 도핑된 텅스텐 | Small rare earth oxide additions like Y2O3 improves sintered density | ≥18.5g/cm |
| 텅스텐-니켈-철 | Ni-Fe 합금으로 뛰어난 최종 밀도 제공 | ≥18g/cm |
| 텅스텐 중합금 | 90-97% W(Ni-Cu-Fe 바인더 위상 포함) | ≥17.5g/cm |
| 텅스텐 복합재 | 금, 탄탈륨, 고갈 우라늄 등과 혼합됩니다. | 최대 21g/cm |
이러한 향상된 배합은 순수 텅스텐을 넘어 맞춤형 특성 조합으로 고성능 옵션을 확장합니다.
구성 텅스텐 분말의
가능한 최고 밀도에 적합한 고순도 텅스텐 분말은 99.95% 이상의 텅스텐을 함유하고 있으며 잔류 불순물이 거의 없습니다:
| 요소 | 최대 콘텐츠 | 역할 |
|---|---|---|
| 텅스텐(W) | 99.95% | 주요 구성 요소 |
| 탄소(C) | 100 ppm | 곡물 성장 억제제 |
| 산소(O) | 100 ppm | 표면 산화물 |
| 구리(Cu) | 10 ppm | 잔류 미량 불순물 |
| 실리카(Si) | 20 ppm | 불순물 |
특수 중합금 등급은 텅스텐과 함께 니켈, 구리, 철 등의 합금을 의도적으로 첨가하여 특성을 더욱 향상시킵니다.
속성 텅스텐 분말의
고밀도 텅스텐 분말을 사용하면 유용한 강도, 경도 및 열적 특성과 함께 극도의 밀도를 자랑하는 그물 모양에 가까운 부품을 제조할 수 있습니다.
물리적 속성
| 속성 | 가치 |
|---|---|
| 밀도 | ≥18g/cm3 |
| 녹는점 | 3380-3410°C |
| 힘 | 최대 1000MPa |
| 경도 | ≥400 VPN |
| 열 전도성 | ∼175W/(m-K) |
| 열팽창 계수 | ∼4.5μm/(m-K) |
이러한 특성은 텅스텐의 고유한 원자 구조에서 비롯되며 열-기계적 무결성이 필요한 고밀도 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다.
기계적 특성
세심한 파우더 압착과 소결로 유리한 기계적 특성을 얻을 수 있습니다:
| 속성 | 가치 |
|---|---|
| 경도 | 최대 550개 VPN |
| 수율 강도 | ∼900 MPa |
| 인장 강도 | 최대 1000MPa |
| 신장 | ∼10% ~ 15% |
| 골절 인성 | ∼20 MPa√m |
| 피로 강도 | 500 MPa |
니켈, 철 등의 합금 원소는 연성, 인성 및 가공 특성을 맞춤화하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
물리적 특성
디자이너에게 유용한 고밀도 텅스텐 분말의 두드러진 물리적 특성:
| 매개변수 | 가치 | 단위 |
|---|---|---|
| 밀도 | 18~19.3 | g/cm3 |
| 전기 저항 | 5.5 | μΩ-cm |
| 열 전도성 | 170 | W/(m-K) |
| 융점 | 3410 | °C |
| 끓는점 | 5930 | °C |
| 비열 | 132 | J/(kg-K) |
초고융점과 열전도율로 극한의 온도에서도 강도와 치수 무결성을 유지할 수 있습니다.
프로덕션 텅스텐 분말의
| 스테이지 | 설명 | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Raw Material Acquisition | The process begins with mining tungsten ore, which primarily consists of wolframite and scheelite. | * Tungsten ores are found worldwide, but major producers include China, Peru, and Bolivia. * Mining methods vary depending on the deposit, but common techniques include open-pit and underground mining. * The mined ore undergoes crushing, grinding, and concentration processes to remove impurities and enrich the tungsten content. |
| 2. Chemical Processing | The concentrated ore is then converted into an intermediate chemical compound suitable for further purification and reduction. | * Ammonium paratungstate (APT) is the most widely used intermediate. It’s produced through a series of chemical reactions involving leaching, filtration, and precipitation. * APT offers advantages like high purity and good handling characteristics. * Other intermediate compounds like tungstic acid or tungsten oxides may also be used depending on the specific production process. |
| 3. High-Purity Oxide Production | Further purification steps ensure the removal of remaining impurities and achieve the desired level of tungsten oxide for reduction. | * APT undergoes additional purification steps like recrystallization or solvent extraction to meet the stringent purity requirements for tungsten powder production. * Tungsten oxides like WO3 (tungsten trioxide) or WO2 (tungsten dioxide) are often the final product of this stage. * The choice of oxide and its specific characteristics can influence the final tungsten powder properties. |
| 4. Hydrogen Reduction | The purified tungsten oxide is then reduced to metallic tungsten powder using hydrogen gas in a controlled furnace environment. | * This stage is the heart of tungsten powder production. Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, taking oxygen away from the tungsten oxide and leaving behind pure tungsten metal particles. * The reduction process occurs in pusher furnaces or rotary furnaces at precisely controlled temperatures (typically between 600°C and 1100°C) and hydrogen gas flow rates. * Careful control of these parameters is crucial for achieving the desired tungsten powder properties like particle size, morphology, and purity. |
| 5. Powder Classification and Finishing | The raw tungsten powder from the reduction furnace undergoes further processing to achieve the final desired characteristics. | * The powder is screened and classified to obtain specific particle size distributions. Different applications require powders with varying particle sizes and morphologies. * Additional processes like milling or granulation may be used to refine the particle size and shape further. * The powder may also be subjected to degassing treatments to remove any residual hydrogen from the reduction process. |
| 6. 품질 관리 | Throughout the production process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure the final tungsten powder meets all the required specifications. | * Chemical analysis determines the elemental composition and purity of the powder. * Particle size distribution and morphology are analyzed using techniques like laser diffraction and electron microscopy. * Other tests may assess properties like density, flowability, and sintering behavior. * Maintaining consistent quality is essential for the performance of tungsten products made from the powder. |
애플리케이션 텅스텐 분말의
| 범주 | 애플리케이션 | 활용되는 속성 | 예제 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial & Manufacturing | Machining & Cutting Tools | 극도의 경도, 내마모성 | – Drill bits – Milling inserts – End mills – Turning tools |
| Dies & Molds | High melting point, thermal stability | – Extrusion dies for wires and filaments – Hot stamping dies – Plastic injection molding tools | |
| 전극 | 높은 융점, 우수한 전기 전도성 | – Inert gas welding (TIG) electrodes – Resistance welding electrodes | |
| Filaments & Heating Elements | 높은 융점, 우수한 전기 전도성 | – Incandescent light bulb filaments – Furnace heating elements | |
| 촉매제 | High surface area, ability to promote chemical reactions | – Ammonia production catalysts – Hydrocarbon processing catalysts | |
| Pigments & Coatings | High density, opacity to X-rays | – Radiation shielding for medical equipment – X-ray contrast agents | |
| 전기 및 전자 | 전기 접점 및 스위치 | High melting point, good electrical conductivity, arc resistance | – Relay contacts – Circuit breaker contacts – High-voltage switchgear contacts |
| 방열판 | 높은 열전도율 | – Electronic component heat dissipation | |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | High density, etch resistance | – Tungsten plugs and vias in integrated circuits – Gate electrodes in transistors | |
| 소비재 | 스포츠 용품 (Golf Clubs, Fishing Weights) | High density for weight distribution | – Golf club weighting for improved swing – Fishing weights for deeper, faster sinking |
| 진동 감쇠 | 고밀도 | – Dampeners in tennis rackets and archery equipment – Vibration dampers in machinery | |
| Advanced Applications | 적층 제조(3D 프린팅) | Fine particle size, good flowability | – 3D printed components for aerospace and automotive industries – Medical implants |
| 원자력 에너지 | High melting point, neutron absorption | – Control rods in nuclear reactors – Nuclear waste shielding | |
| Military & Defense | 갑옷 관통 관통탄 | High density, extreme hardness |
사양
고밀도 텅스텐 분말에 대해 정의된 주요 매개변수입니다:
Grades of Tungsten Powder
| Grade Designation | Average Particle Size (Microns) | Purity (Minimum % Tungsten) | 애플리케이션 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrafine Tungsten Powder | < 1.0 | ≥ 99.95 | – Thermal Spray Coatings for turbine blades and other high-wear applications due to excellent sinterability and flowability. |
| 1.0 – 3.0 | ≥ 99.95 | – Diamond Tools with superior wear resistance and sharpness for cutting and grinding hard materials. | |
| 3.0 – 5.0 | ≥ 99.9 | – Electronic Substrates with minimal impurities for high electrical conductivity and thermal stability in integrated circuits. | |
| Fine Tungsten Powder | 5.0 – 10.0 | ≥ 99.5 | – Cemented Carbide Cutting Tools offering a good balance between hardness, toughness, and fracture resistance for machining various materials. |
| 10.0 – 15.0 | ≥ 99.0 | – Heavy Duty Electrical Contacts requiring high melting point, arc resistance, and electrical conductivity in power switching applications. | |
| 15.0 – 22.0 | ≥ 98.5 | – Electrodes for Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding due to their ability to produce a stable arc and concentrated heat. | |
| Medium Tungsten Powder | 22.0 – 32.0 | ≥ 98.0 | – Penetrators and Kinetic Energy Projectiles leveraging tungsten’s high density for superior armor penetration. |
| 32.0 – 45.0 | ≥ 97.0 | – Radiation Shielding Materials in medical equipment and nuclear facilities due to tungsten’s ability to absorb X-rays and gamma rays. | |
| Coarse Tungsten Powder | 45.0 – 75.0 | ≥ 96.0 | – Ballast Weights for counterweights and vibration dampeners utilizing tungsten’s high density for compact size and effectiveness. |
| > 75.0 | ≥ 95.0 | – Shot Peening Media for surface strengthening metal components through a cold working process. |
Standards of Tungsten Powder
| 속성 | 설명 | 중요성 | 일반적인 표준 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 순도 | Tungsten powder purity refers to the percentage of tungsten metal (W) present in the powder by weight. Impurities can significantly affect the physical and mechanical properties of tungsten products. | Higher purity generally translates to better performance in applications that rely on properties like electrical conductivity, melting point, and strength. However, extremely high purity may not always be necessary or cost-effective. | – High Purity (99.9% W and above): Used for electronics, filaments, and electrodes where excellent electrical conductivity is crucial. – Standard Purity (99.5% W – 99.9% W): Suitable for various applications like cemented carbide cutting tools, heat sinks, and radiation shielding. – Lower Purity (Below 99.5% W): Used in some specific applications like plastic fillers or as a raw material for further purification. |
| 입자 크기 및 분포 | Particle size refers to the average diameter of individual tungsten particles in the powder. Particle size distribution describes the variation in particle sizes within a powder sample. | Particle size and distribution significantly impact the processing behaviour and final properties of tungsten products. For example, finer particles can offer better sinterability but may be more challenging to handle. | – Micron-Sized Powders (1 – 50 microns): Commonly used for cemented carbide production, thermal spraying, and additive manufacturing. – Submicron Powders (Below 1 micron): Used in applications requiring high surface area, like catalysts and conductive coatings. – Nano Powders (Below 100 nanometers): Emerging area with potential applications in electronics and composite materials. |
| 겉보기 밀도 | Apparent density represents the weight of tungsten powder per unit volume, considering the spaces between particles. It influences how much powder can be packed into a mold and the final density of the sintered product. | Higher apparent density allows for more efficient use of powder and can lead to denser final products with improved mechanical properties. | – High Density Powders (>10 g/cm³): Used for applications requiring high strength and wear resistance, like cemented carbide tools. – Standard Density Powders (7 – 10 g/cm³): Commonly used for various applications where a balance between density and processing ease is desired. – Low Density Powders (<7 g/cm³): May be used in applications where loose packing or flowability is important, such as some thermal spraying processes. |
| 유동성 | Flowability refers to the ease with which tungsten powder can move and be poured. It is crucial for efficient handling and processing in various applications. | Good flowability ensures smooth powder feeding in machinery and minimizes segregation of different particle sizes within the powder. | – Free-Flowing Powders: Achieved through specific particle size distribution and surface treatments to minimize particle-particle interactions. – 첨가제: May be used to improve flowability by reducing friction between particles. |
| 형태학 | Morphology refers to the shape and form of individual tungsten particles. | Particle morphology can influence packing behaviour, sintering characteristics, and the final microstructure of tungsten products. | – 구형 분말: Offer good packing density and flowability. – Angular Powders: May create a more interlocking network during sintering, potentially leading to improved strength. – Dendritic Powders: Can be used for specific applications where their branching structure offers advantages. |
| 산소 함량 | Oxygen content refers to the amount of oxygen present in the tungsten powder, typically as oxides. Excessive oxygen can affect the final properties of tungsten products. | – Low oxygen content is generally desired for most applications to ensure optimal performance. – Strict oxygen limits are often specified for high-performance applications like electronics and filaments. |
|
| 탭 밀도 | Tap density is a measure of the packing density of tungsten powder achieved through a standardized tapping process. It provides an indirect measure of flowability and apparent density. | – Higher tap density indicates better packing efficiency and can be used as a quality control parameter. | – Industry standards often specify minimum tap density requirements for different tungsten powder grades. |
가격 책정
고밀도 용도에 적합한 텅스텐 분말의 대표 가격입니다:
| 등급 | 가격 |
|---|---|
| 초미세먼지 | kg당 $800 ~ $1200 |
| 서브미크론 | kg당 $500 ~ $900 |
| 괜찮아요 | kg당 $100 ~ $250 |
| Medium | kg당 $50 ~ $150 |
| 무거운 합금 | kg당 $40 ~ $100 |
입자 크기가 작아지고, 순도가 높아지고, 특수 도펀트가 첨가되고, 수량이 줄어들면 비용이 증가합니다. 재활용 스크랩 파우더는 더 저렴합니다.
장단점
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| Unmatched High Melting Point: Tungsten powder boasts the highest melting point of any metal, reaching a staggering 3,422°C (6,192°F). This exceptional property allows it to excel in applications exposed to extreme temperatures, like furnace linings, rocket nozzles, and heat shields for spacecraft re-entry. | Costly Investment: Extracting and processing tungsten is a complex procedure, leading to a higher price tag compared to more common metals. This can be a significant hurdle for applications where cost is a major factor. |
| Superior Heat and Electrical Conductivity: Tungsten powder excels in conducting both heat and electricity efficiently. This makes it ideal for applications requiring efficient thermal management, like heat sinks in electronics, or electrical components like filaments in incandescent lamps and electrodes for welding. | Dense and Demanding: Tungsten’s remarkable density, a direct consequence of its tightly packed atomic structure, translates to its powder form as well. This high density can pose challenges during processing. Specialized techniques and equipment might be necessary to handle and shape tungsten powder effectively. |
| Exceptional Wear and Corrosion Resistance: Tungsten powder exhibits outstanding resistance to wear and tear, alongside exceptional corrosion resistance. This makes it perfect for applications requiring exceptional durability in harsh environments, like armor-piercing projectiles, drill bits for tough materials, and components used in chemical processing plants. | Potential Health Risks: Tungsten powder, if inhaled, can irritate the lungs and potentially lead to health complications. Strict safety protocols and proper ventilation are crucial when working with tungsten powder to minimize exposure risks. |
| Tailorable Alloying Potential: Tungsten powder readily forms alloys with various metals, significantly enhancing their properties. This allows engineers to create custom-designed materials with specific combinations of strength, hardness, and heat resistance for applications like high-performance cutting tools and jet engine components. | Limited Global Supply: The primary source of tungsten is geographically concentrated, with China dominating global production. This can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and potential price fluctuations. |
| 생체 적합성 애플리케이션: Tungsten exhibits good biocompatibility, making its powder form suitable for certain medical applications. For instance, tungsten-based implants can be used for hip replacements due to their exceptional strength and wear resistance. | Specialized Suppliers: Due to the unique properties and potential safety concerns of tungsten powder, sourcing it from reputable and experienced suppliers is essential. These suppliers can provide high-quality, well-characterized powder alongside technical support to ensure safe handling and optimal performance in the desired application. |
| Emerging Applications in 3D Printing: Tungsten powder is finding new applications in the rapidly advancing field of additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. Its unique combination of properties makes it suitable for printing high-performance metal parts for aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. | Counterfeit Concerns: The high value of tungsten powder can attract manufacturers of counterfeit products. Working with qualified suppliers with rigorous quality control practices helps mitigate the risk of receiving inferior or impure material. |
공급업체
전 세계적으로 고밀도 텅스텐 및 텅스텐 합금 분말을 공급하는 저명한 판매자 및 제조업체는 다음과 같습니다:
| 회사 | 위치 |
|---|---|
| 버팔로 텅스텐 | 미국 |
| 울프램 컴퍼니 | 오스트리아 |
| Plansee 그룹 | 유럽 |
| 중서부 텅스텐 | 미국 |
| 샤먼 텅스텐 | 중국 |
| JX 일본 | 일본 |
| 도시바 머티리얼즈 | 일본 |
| GTP 셰퍼 | 독일 |
이 기업들은 신뢰할 수 있는 세계적 수준의 파우더를 상업용 시장에 공급합니다.

자주 묻는 질문
| 질문 | 답변 |
|---|---|
| 고밀도 텅스텐 분말이란 무엇인가요? | 텅스텐 분말의 밀도는 18~19.3g/cm3으로 모든 금속 분말 중 가장 높습니다. |
| 고밀도 텅스텐 분말은 어떻게 제조되나요? | 원하는 입자 크기를 위한 특수 밀링과 결합된 정제된 산화 텅스텐의 감소 |
| 고밀도 텅스텐 분말은 어떤 용도로 사용되나요? | 평형추, 방사선 차폐, 밸러스트, 가중치 화합물, 진동 감쇠 부품 등을 제작합니다. |
| 고밀도 파우더에는 어떤 종류가 있나요? | 순수 텅스텐, 희토류 산화물로 도핑된 텅스텐, 텅스텐-니켈-철 합금, 텅스텐 중합금 등이 있습니다. |
| 고밀도 텅스텐 분말의 장점은 무엇인가요? | 다른 파우더와 비교할 수 없는 컴팩트한 부피의 극대화된 밀도, 복잡한 부품을 그물 모양으로 제조할 수 있습니다. |
| 텅스텐 파우더를 사용할 때 어떤 한계가 있나요? | 텅스텐 카바이드보다 상대적으로 낮은 경도, 제한된 인성 및 연성으로 인해 가공에 어려움이 있습니다. |
| 고밀도 텅스텐 분말은 납과 같은 기존의 고밀도 소재와 비교했을 때 어떤 차이가 있을까요? | 독성이 있는 납보다 안전하고, 납보다 녹는점이 높으며, 밀도가 비슷한 귀금속에 비해 경제적으로 가격이 저렴합니다. |
요약
원소 금속 중 밀도가 가장 높은 고순도 텅스텐 분말은 이전에는 불가능했던 소형 프로파일을 필요로 하는 무게에 민감한 응용 분야를 위한 고유한 기능을 설계자에게 제공합니다. 분말 제조, 프레스, 소결 및 2차 가공의 발전으로 취성 한계를 극복하여 더 폭넓게 사용할 수 있게 되었습니다. 혼합 및 합금은 고밀도가 강도, 경도 및 열적 혈통과 매우 밀접하게 결합하는 까다로운 전기, 원자력, 자동차 및 항공우주 분야에서 물리적 특성을 추가로 맞춤화할 수 있습니다.
지속 가능한 공급원이 신뢰할 수 있는 글로벌 공급망을 뒷받침함에 따라 설계자들은 이제 무거움과 소형화가 함께 가치를 창출하는 산업 전반의 정밀 엔지니어링 기능을 위해 텅스텐 분말의 극한 밀도를 활용하고 있습니다. 텅스텐의 전략적 중요성이 커짐에 따라 선도적인 제조업체들은 향후 10년간 밀도 임계값을 20g/cm3를 넘어서는 것을 추구할 것입니다.