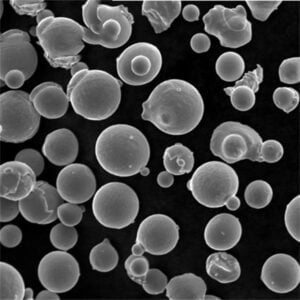
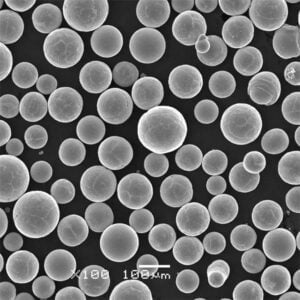
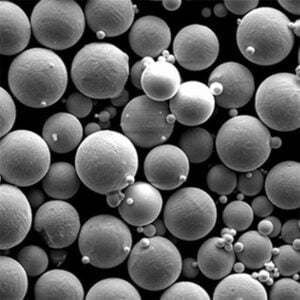
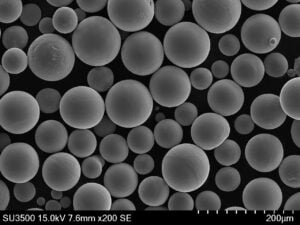
원자화된 금속 분말 enable manufacturing methods like additive manufacturing and thermal spray needing feedstock with tailored particle sizes, shapes and metallurgical properties. This guide reviews production processes, specifications, suitable metals, usages, vendor selection and alternatives around commercial atomized powders.
atomized metal powders Overview
Atomization converts molten metal streams into fine spherical droplet sprays rapidly cooling into powder form. Key attributes versus alternatives like chemical precipitation include:
- Controlled particle size distribution from 10 microns to 300+ microns
- Ability to process reactive alloys in inert gas atmospheres
- Rapid solidification producing finer microstructures
- Lower oxygen and nitrogen impurity levels
- Cost-effectiveness from high powder yields targeting 50%+
- Adaptability preparing most commercial metals and alloys
Understanding available production methods, specifications, applications and economics enables properly leveraging atomization’s benefits and limitations when selecting metal powders.

Methods for Atomizing Metal Powders
Industrial scales require atomization through either gas, water or centrifugal processes:
| 방법 | 설명 | 사용된 금속 | 입자 크기 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Supersonic inert gas jets convert metal stream into powder | Most common. Reactive materials compatible | 10 μm – 150 μm |
| 물 | High pressure water disintegrates molten metal exposing it to rapid quench | Primarily copper and iron. Limited reactive materials | 5 μm – 350 μm |
| Centrifugal | Molten metal accelerated outwards from a spinning disk. Rapidly cools into powder. | Most metals compatible. Lower reactive capability | 45 μm – 1 mm+ |
표 1. Commercial scale atomization techniques for producing metal powders alongside output traits
Each technique provides unique advantages around particle sizing, powder yields, quench rates and compatibility across the expansive metals universe.
Metals and Alloys Compatible with Atomization
Atomization viably processes most commercial metals and alloys including:
- Titanium alloys containing aluminum and vanadium
- Superalloys like nickel-based Inconel and cobalt-based Haynes alloys
- High temperature metals such as molybdenum, tungsten and tantalum
- Reactive elements like chromium and manganese
- Precious metals including gold, silver and platinum
- Refractory metals: niobium, zirconium and hafnium
- Common austenitic stainless steels 316L and 304L varieties
Strong chemical reactivity under molten states does restrict applicability for some elemental metals like pure manganese or chromium. But blending into alloys mitigates reactivity downsides through atomization compatibility – an advantage over other powder production approaches.
특성 및 속성 원자화된 금속 분말
Atomization outputs metal powders with tailored powder characteristics meeting production process needs:
입자 크기 분포
- Tunable from 10 microns to 1 mm sizes, sievable into precise fractions
파티클 모양
- Predominantly spherical morphologies especially with inert gas atomization
Internal Porosity
- Rapid solidification and inert processing minimizes trapped gases creating voids
화학적 순도
- 99%+ achievable for inert gas atomized materials. Water atomization slightly less.
표면 산화물
- Water atomization entrains 5-15X more surface oxygen contamination versus inert atomizing protections
Microstructural Phases
- Rounded by rapid quenching compared to cast ingot counterparts
The ability optimizing particle size and shape parameters while retaining high chemical cleanliness and favorable microstructures suits atomized metal powders to additive manufacturing feedstocks where such characteristics critically influence process success and final part performances realized.
Metal Powder Size Specifications from Atomization
Atomized metal powder lots classify based on particle size distributions. Common sieve sizes include:
| 메시 | 미크론 크기 | 일반적인 사용법 |
|---|---|---|
| +100 | >150μm | Thermal spray components and coatings |
| -100 +325 | 105 – 150 μm | Hot isostatic pressing precursors |
| -325/+500 | 32 – 105 μm | Binder jet/cold spray 3D printing |
| -500 | <32 μm | Powder bed fusion additive manufacturing |
표 2. Particle size categories for classified atomized metal powders aligned to manufacturing process compatibilities
Most proprietary atomization systems target 50%+ yields of powder collected within manufacturing grade specifications after sieving separation of oversize and undersize fractions recycled back into the process melt stream.
Industry Specifications for Atomized Metal Powders
Various associations maintain compositional, chemical and physical property standards for commercial metal powders including:
| 엔티티 | 표준 번호 | 적용되는 금속 |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM 국제 | F3049 | Titanium and Titanium Alloys |
| ASTM 국제 | F3056 | Nickel and Nickel Alloys |
| ASM International | MMPDS-06 | Multiple Metal Materials Properties |
| APMI Int’l | ANSI/APMI B.101 | Copper and Copper Alloys |
표 3. Trade groups offering specifications applicable towards sieved chemistries and powder metrics useful for quality assurance across atomized materials
Additionally, individual manufacturers provide narrowly scoped specifications covering unique alloys or specialty characteristics like maximum oxygen or nitrogen thresholds critical for reactive alloy processing.
인증 범위를 검토하면 표준이 구매자가 요구하는 조성 창, 홀 유량과 같은 허용 가능한 분말 특성, 분무 기능 및 후속 생산 공정 요구 사항과 일치하는 화학적 순도 수준을 적절히 포함하도록 보장합니다.
Applications and Uses for Atomized Metal Powder
Offering a backbone feedstock for industrial manufacturing, key metal powder applications include:
적층 제조
- Aerospace components – turbine blades, airfoils
- Medical implants – hip, knee and dental replacements
- Tooling – Lightweight conformally-cooled plastic injection molds
- Chemical reactors – High surface area structured catalyst supports
열 스프레이
- Oil & gas anti-corrosion coatings – downhole tools
- Printing roll surfaces resisting abrasion
- Chrome replacement automotive surfaces
- High release low friction architectual glass molds
분말 야금
- Automotive transmission gears and engine components
- Permanent magnets in motors and sensors
- Diamond tooling inserts and cutting tools
- Electrical contacts leveraging specific conductivity
The foundation feedstocks serve any application demanding combined chemistry and refined powder texture capable of consolidation into end-use geometries.
Atomized Metal Powder Manufacturers and Vendors
Leading global suppliers providing atomization capabilities for medical, aerospace and industrial markets include:
| 회사 | 위치 |
|---|---|
| 샌드빅 | 스웨덴 |
| 카펜터 기술 | 미국 |
| 프렉스에어 | 미국 |
| 회가나스 | 스웨덴 |
| 파이로제네시스 | 캐나다 |
| 에라스틸 | 프랑스 |
표 4. Notable manufacturers offering atomized metal powder production from various process technologies
Secondary brokers also distribute powders but best practice procures directly from mills providing lot traceability and eliminating intermediary quality risks contaminating materials between major producers and end part makers.
대상 가격 원자화된 금속 분말
Pricing varies based on composition, particle size distribution, production volume and quality:
| 재질 | Price per Kilogram |
|---|---|
| 티타늄 Ti64 | $50 – $150 |
| 니켈 초합금 | $50 – $250 |
| 스테인리스 스틸 | $5 – $30 |
| 공구강 | $2 – $15 |
Niche alloys made in small batches demand higher prices offsetting furnace changeovers. Commodity metals like stainless steel reprocessed at high volumes offer lowest cost. But buyers validate fair relative value by comparing resulting performance increases against usage in final components.
원자화된 금속 분말의 장단점
장점 of atomized metal powders:
- Controlled particle size distributions at commercial production rates
- Spherical powder morphology from inert gas processes
- Rapid solidification and inert processing provide chemical cleanliness
- Adapts to wide array of specialty alloy feedstock needs
제한 사항 to consider:
- 10-100X feedstock cost increases over wrought product forms
- Limited on-demand flexibility with long lead time needs
- Attention required not over-specifying powder qualities or costs balloon
Properly weighting benefits against limitations helps avoid overspending just to use buzzword technologies yielding no appreciable customer value.

Comparisons to Other Metal Powder Production Methods
Tradeoffs between common metal powder manufacturing approaches:
| 방법 | 확장성 | 비용 | 순도 | Particle Control | Metals Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 원자화 | 매우 높음 | $$$$ | 높음 | 우수 | Some elemental metals |
| HDH | 낮음 | $ | Medium | Poor | Pyrophorics |
| 전기 분해 | 높음 | $$ | 중간에서 높음 | 보통 | |
| Chemical Precipitation | 높음 | $ | Medium | Poor |
표 5. Qualitative comparisons across commercial scale metal powder production methods
While producing significant volumes with optimized powder characteristics, atomization does command pricing premiums that could limit adoption in cost-sensitive industries like autos.
자주 묻는 질문
Q: What is the primary purpose of atomization for metal powders?
A: Precisely controlling particle size and shape parameters otherwise random across other techniques to suit strict requirements of additive manufacturing processes.
Q: Do recycled metal powders retain original properties?
A: Yes, factors like oxygen pickup and microstructural phases largely unchanged allowing reuse to supplement virgin production powders.
Q: Can gas atomization achieve sub 10 micron powder sizes?
A: Extremely fine distributions down below 5 microns possible but at very low yields not economical for commercial additive manufacturing usage as surface area drives reactivity.
Q: What industries use atomized metal parts?
A: Aerospace, medical, automotive, and oil/gas all leverage tailored alloys and microstructures produced from atomization process uniqueness.